There are various types of surface defects found in an RCC structure, but here we discussed only Blowholes/Surface voids/Bugholes in concrete. Concrete is a versatile material, and its durability depends mainly on quality control during production, placing and condition of exposure. After completion of the structure, various operations that may be required to do on it to preserve the intended load-carrying capacity and to ensure correct functioning, durability, aesthetic appearance and continuity of safety. Before any repair and maintenance work is taken up, the cause of damage and the amount of damage to the structure must be determined by thorough inspection.
Also, Read: Maintenance of Bridges – General Planning & procedure

Also, Read: Rusting of Iron Rebar in Concrete – Special Repairing
What is Blowholes/Surface voids/Bugholes in Concrete Surface?
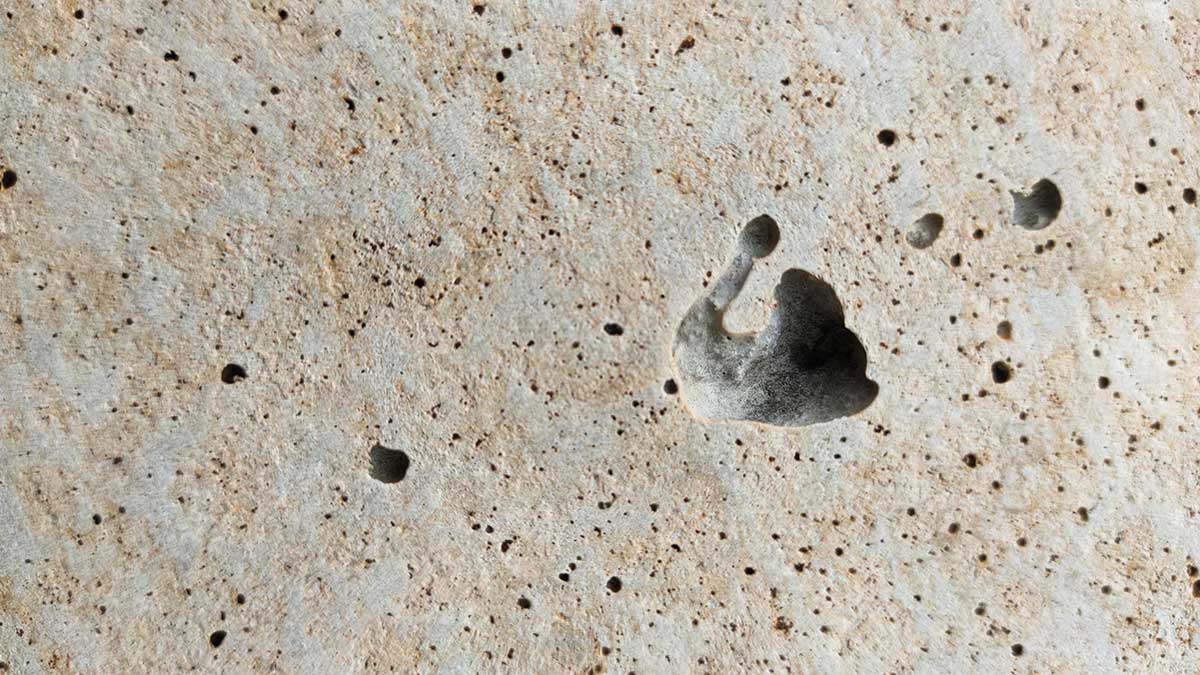
Surface voids are small pop-outs or holes that appear on the outer surface of the concrete due to entrapped air. A significant challenge of the concrete industry today is to control the concrete surface quality fulfilling all the design mix criteria. Sometimes these voids may be unappealing to the public eye, but it is essential to repair for bridge/structural construction work.
Causes:
Generally, Blowholes/Surface voids/Bugholes formed due to the following reason:
- Improper vibration practice
- non-permeable formwork
- Improper mix design
- High slump
- Aggregate quality
- Admixture property
- Concrete mix temperature
Also, Read: Nondestructive Testing of Concrete – Methods & Guidelines
Repairing Techniques:
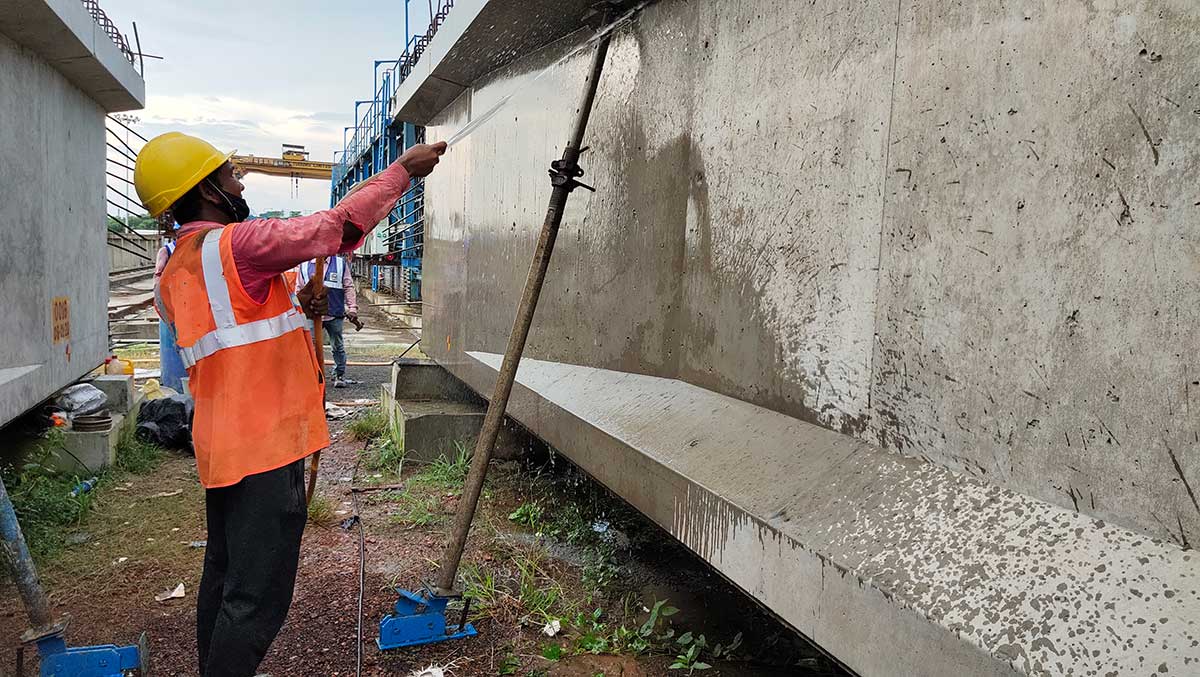
Sometimes in portions of the vertical, bottom and inclined surfaces of precast/cast-in-situ members, the appearance of small Blowholes/Surface voids/Bugholes due to air bubbles are observed. These fall under surface defects of minor nature and shall be finished after de-shuttering as envisaged in 01.1713 of specification of works (MORTH-V, 2013).
Though specification prescribes filling these with cement mortar – but in some cases because of the importance of the structure and its future durability it should be sealed and finished with Polymer mortar using Polymer Latex of a reputed manufacturer in prescribed dosage for gauging the mortar.
Note: Polymer Mortar repair is also covered under Cl. 2804.2 of Specifications for Repair work of more serious defects such as spoiling, and hence shall be superiorly qualified for Finishing of surface bubbles as envisaged in this procedure.
Materials Required for Repairing:
- Cement: OPC 43/53 Grade
- Sand: Approved river sand sieved to pass 2.36mm
- Polymer Latex: Polymer Latex of a reputed manufacturer
- Water: From Approved source (Borewell)
Surface Preparation: The area of the surface bubbles/blowholes/entrapped surface air voids shall be thoroughly cleaned by wire brushing, and all dust or powder generated in the process washed off with water.
Also, Read: Causes, Prevention and Repair of Concrete Surface Defects

Also, Read: What is Prestressing of Concrete? – Method with Calculation
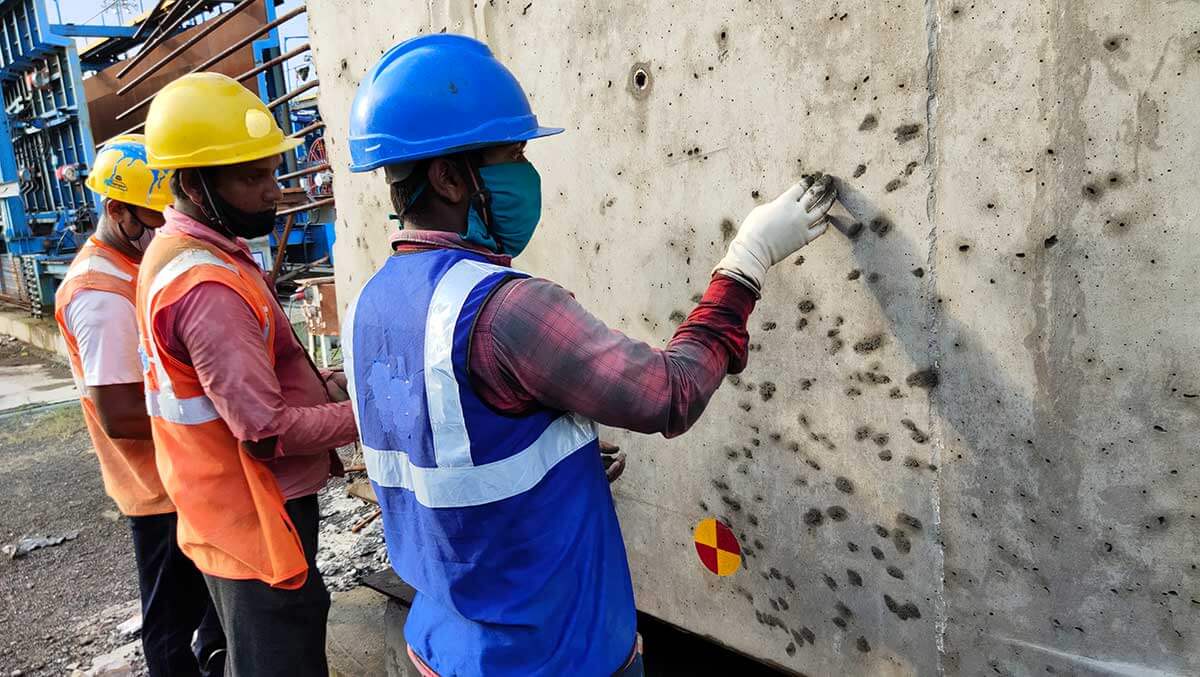
Repair Using Polymer Mortar:
Proportioning:
- Polymer mortar shall consist of Cement and fine sand (passing 2.36mm Sieve) in the proportion of 1 : 3 (Cement: Sand ).
- This mortar shall be drily mixed thoroughly and gauged with liquid polymer solution prepared in the ratio 1:6 (1-Part Polymer Latex diluted with 6-parts water) as per the manufacturer’s recommendation.
- Small quantities of White cement or lime may be used as part of the Cementitious content to reduce colour differences if required.
Application:
- The mortar shall be prepared to a stiff consistency with just enough polymer solution to allow moulding of the mortar into cohesive balls by hand without sagging or breaking up.
- The Polymer mortar shall be filled with hand or sacking pad by working into the small air bubble voids with sufficient pressure. It shall be thoroughly tamped in and levelled with a trowel.
- This will be allowed to set and harden for a few hours, then cured by keeping moist for 24hrs, and subsequently by frequent sprinkling up to 3 days.
- After 5 to 7 days, the area surrounding the filled bubble voids can be lightly rubbed with carborundum stone if required to make any irregularities even.
Also, Read: Bridge Inspection Types – Objectives and Guidelines

Also, Read: Formula for Development Length, Anchorage and Lapping Length
Blowholes/Surface voids/Bugholes are rarely a structural problem; but, if not marked, they can increase the possibility of future problems like Spalling, Delamination, Leaching etc.