Road Kerb:
Road Kerb is a physical or painted concrete or stone structure typically located at the edge of a road constructed to prevent vehicles from leaving the carriageway. Sometimes it provides separation between two adjacent lanes.
Road Kerb profile and Types:
Kerbs confirm the barrier between the carriageway and the shoulder or islands or footpaths. The height of road kerb above the pavement edge varies from 100mm to 200mm as per requirement. There are different types of road kerb profile, but the following profiles are generally used for Highway Construction.
- Half-battered kerb.
- Bull-nosed kerb.
- Splayed kerb.
- Square kerb.
Also, Read: Wet Mix Macadam Construction and Quality Control
Type of kerb:
- Natural stone kerb
- Precast concrete kerb
- Cast in-situ concrete kerb

Also, Read: Concrete Subbase Course – DLC Construction
Kerb Construction Methodology:
Materials for Road Kerb:
The following construction materials shall be used for the activity:
Cement:
Ordinary Portland Cement of 43 and 53 Grades conforming to IS:8112 and IS:12269 codes respectively and shall meet all physical specification.
Coarse and Fine Aggregate:
Coarse and fine aggregate conforming to IS: 383 shall be used. Gradation of combined aggregates of different sizes shall be following IS 383 and MORTH sec. 1000. Different mechanical properties of coarse aggregates and properties of fine aggregate are to be conformed to IS: 383 and the tests shall be conducted as per relevant test codes.
Water:
Potable water shall be used for concreting and shall be conforming to MORTH Specification.
Concrete :
The concrete of grade M 20 to be used for the kerb shall be produced at the batching plant as per the approved mix design. The concrete shall be loaded on to the transit mixer directly from the batching plant and transported to the laying location.
Also, Read: Granular Sub Base Construction and Quality Control
Plant, Equipment and Machinery For Kerb Construction:
- Transit Mixer
- Concrete Batching Plant
- Water Tanker
- Kerb cutting machine
- Survey related equipment
Specification of Kerb Casting Machine:
- The engine is of continuous rating with four cylinders water-cooled diesel of 29 HP.
- It has a separate pump for a drive and other functions.
- It has a hydraulic vibrator and 3-bank pressure compensated controller.
- It is having a sensor for controlling grade, line & slope with remote slope set.
- It has a single lever speed and direction control system.
- It is having a speed of 6 to 10 Mts. per minute.
- It has a quick fit mould system with an optional floating skid.
- Sensor adjustment is easy to adjust.
- The control console is operator friendly.
Also, Read: Prime Coat and Tack Coat using Cationic Bitumen Emulsion for Road Work
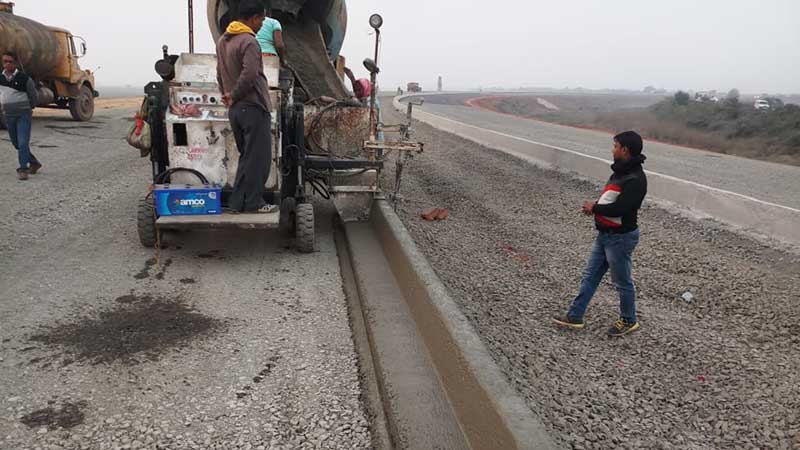
Kerb Construction Operations:
- Mark the lines, level, and adjust the sensor of the kerb casting machine accordingly. Put the pegs at every 5-meter interval and mark the levels on it. These pegs are then joined with metal wire.
- The concrete shall be produced in the batching plant as per the approved mix formula.
- The concrete shall be loaded onto the transit mixers directly from the Batching plants for transporting to the kerb location.
- The kerb shall be laid on a firm foundation of 150mm thick grade M10 concrete cast-in-situ and extending 50mm beyond the kerbstone.
- The cast-in-situ kerb shall be constructed with Arrow 770 XL kerb casting machine in all situation except at location where continuous casting with equipment is not practicable. In those situations, precast concrete blocks shall be used.
- Arrow 770 XL kerb casting machine is capable of laying the kerbs in required cross-section and producing a well compacted mass of concrete free of voids and honeycombs.
- In the median portions in the straight reaches, the kerb shall be cast continuous lengths before Dense Bituminous Macadam (DBM) laying. In the portions where the footpath is provided, and if the slope of the carriageway is towards the median, there shall be sufficient gap/recess left in the kerb to facilitate drainage opening.
- After laying the kerbs and just prior to hardening of the concrete, saw cut grooves shall be provided at 5m interval.
- Vertical and horizontal tolerance with respect to true line and level shall be +/- 6 mm.
- Curing of kerb shall be done by brushing it with curing compound and spread the hessian cloth over it and keeping it moist for five days.
Also, Read: Dense Bituminous Macadam (DBM) Construction Requirements

Purposes of Road Kerb:
As an element of roads and highways, kerbs serve a number of purposes:
- Working as a barrier
- Helps to provide road drainage
- Prevent accident
- prevents encroachment of parking
- provide separation between two adjacent lanes
- Help to prevent unnecessary traffic movements