What is Well Foundation?
Well foundation is being used for 100 of years as a deep foundation which is generally provided below the water level for bridges/heavily loaded structures since Roman and Mughal periods. Well foundation is beneficial for bridge piers, particularly in case of scouring river beds. The various improvised technique of well construction has emerged with the availability of modern equipment which has enabled a reduction in construction time.

- Well foundation Known to have its origin in India.
- Moghal monuments, including the Taj Mahal, have got well foundation.
- The largest size of well foundation was constructed on San Francisco Oakland Bridge in 1973, which is (29.6m x 60.10m) having sinking depth of 73.8m.
Well Foundation vs Pile Foundation:
- Well foundations provide a stable and massive foundation for heavy loads as against a cluster of piles which are slender and weak individually.
- Wells have a large cross-sectional area and high bearing capacity.
- Piles cannot be driven through boulder strata found at greater depth, whereas it is possible to sink wells under such conditions.
- Wells are hollow and have a massive moment of inertia with the minimum cross-sectional area. They can resist large horizontal and vertical loads even when the unsupported length is high on scouring river.
- The minimum size of well foundation is limited due to dredge hole size, which must be big enough to enable grab to work and to provide necessary sinking effort. Thus, uneconomical for small loads.
- The construction time of well foundation is much higher compared to the pile foundation.
Also, Read: Tolerances for Foundation Piles – Important Guidelines
Types of Well Foundation:
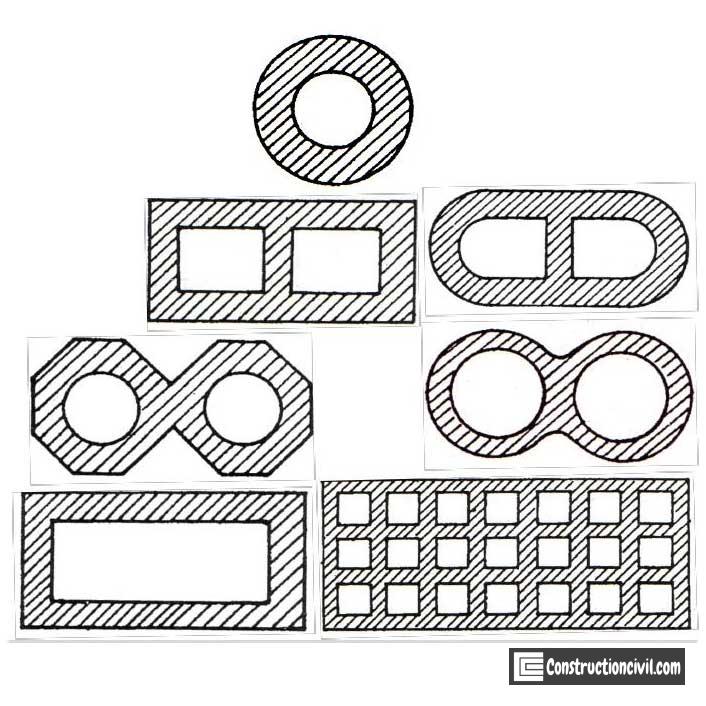
Types of Well Foundation Depending on Shapes:
Wells can be of different types depending on their cross-sectional shapes which are as follows.
- Circular
- Double D
- Double octagonal
- Twin Circular
- Single/ double/ multiple cell rectangular Box well: In this type of well top is open but the bottom is close during construction. This type of well can be used when the load is not very heavy.
Advantages of Circular Well:
Circular type is by far the most commonly used type of well foundation because:
- Simplicity in construction
- least tilt & shift
- weight per sq. meter of the surface area is the highest not required high sinking effort
- Uniform moment of resistance in all directions, etc.
Types of Well Foundation Depending on Construction Method:
Depending on site condition and construction methodology, the well foundation can be classified in following types:
Open caisson or open well:
The processes of sinking are continued till the well reaches the required depths/founding level(RL). During the construction top and bottom portion are opened, once the well is reached at the ground surface or the required depth. The bottom part is sealed with concrete which is known as the bottom plug, and the dredge hole is filled with sand.
Land Well:
Most conventional type, easy for construction, adopted when natural land is available during the construction period.
Island Well:
Similar to land wells, but in deep water where an artificial island can be constructed and maintained during the entire construction period. Generally possible where the depth of water is up to 6m and the velocity of water is within 1m/sec.

Floating Caisson:
It is a special type of well foundation, and where it is not possible to construct and maintain the island during the entire construction period.
The disadvantage of this open well:
If the boulder deposit/Rock is there in the ground surface or the bottom of the water body, then it isn’t easy to in possess or progress the construction of this type of well.
Pneumatic Caisson:
It is closed at the top and opens at the bottom. Complete water is pushed out from the caisson by compressed air. Working chamber and shaft are made air-tight for the construction worker to carry out excavation work underneath. Maximum depth may be 33.00m due to risk to the lives of the worker and team.
Disadvantages:
- In this type of well foundation, construction cost is relatively high.
- The depth of penetration below water level is limited to about thirty-five meter.
- Higher pressure under the working chamber is beyond the endurance of the human body.
Components of Well Foundation:
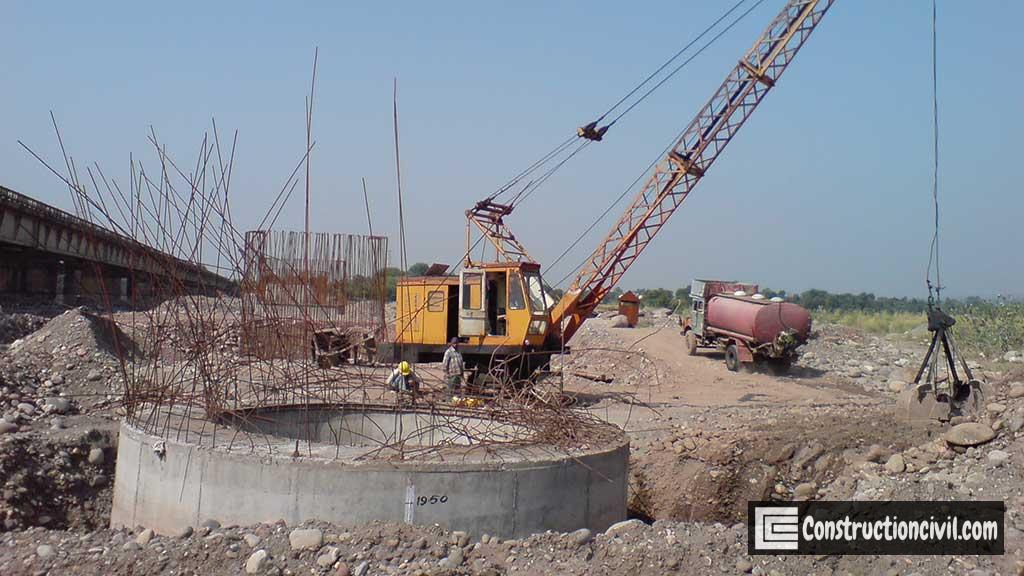
Cutting Edge:
It is the lowest part of the foundation well, and fabricated in the yard as per approved drawing. Cutting edge shall be fabricated in a number of segments depending upon circumference and ease of handling and transport. Cutting edge helps to cuts the soil during the sinking operation.

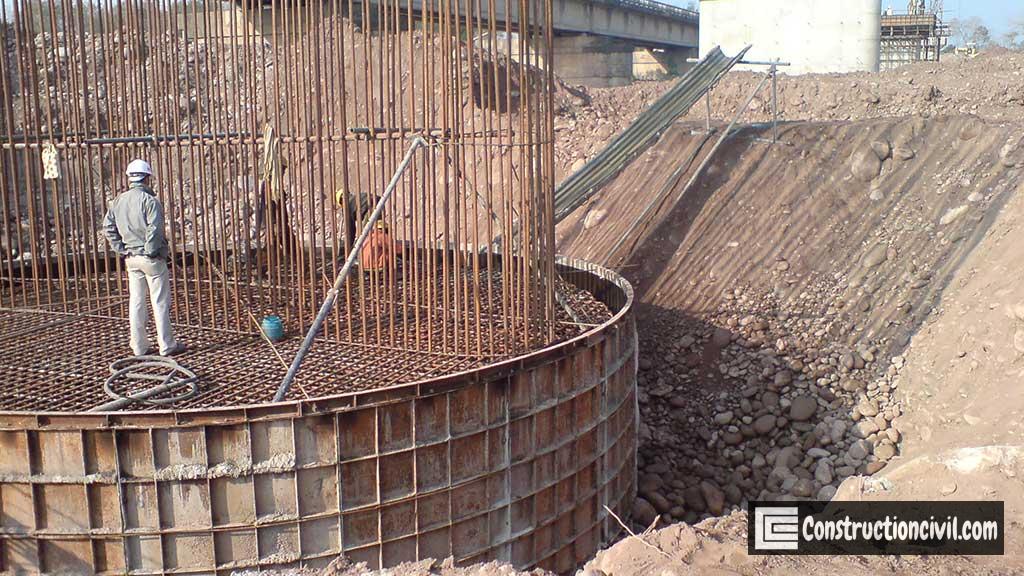
Well Curb:
Well Curb is a RCC ring beam-type component of well having a steel cutting edge below. Vertical cross-section of the well curb is wedge-shaped, which helps during the well sinking. The curb supports well steining, and the steining is kept slightly projected outer side to reduce the skin friction during well sinking.
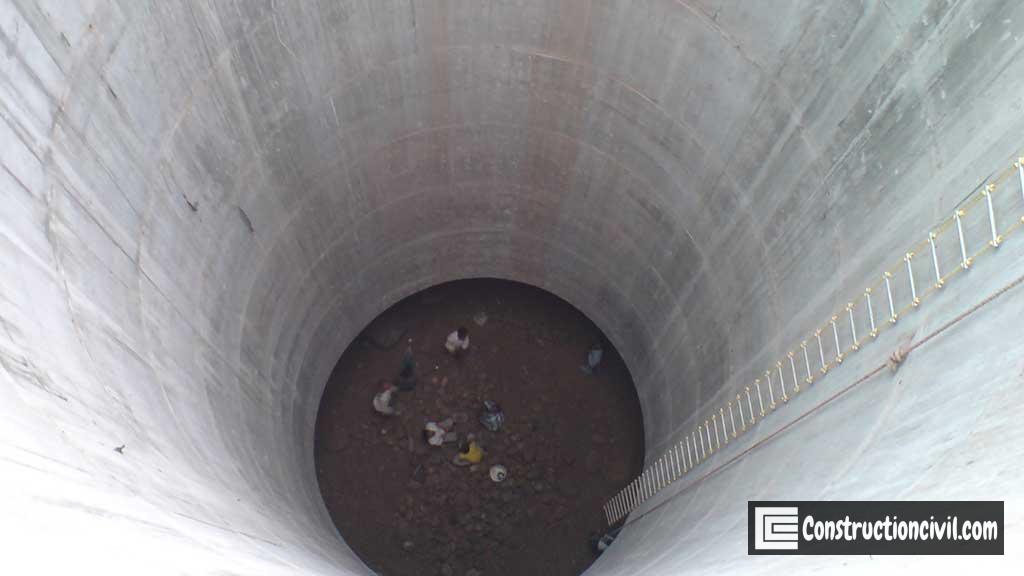
Well Steining:
Steining is a wall or shall type of structure made up of RCC, and which helps to transfer the load to the curb. It serves as an enclosure for excavating the soil for the penetration of the foundation well.
Bottom Plug:
After completion of sinking, the bottom of the foundation well is plugged with the help of concrete. The well curb confines the bottom plug, and functions like a raft against soil pressure from below.
Back-filling:
The well is dewatered after setting of bottom plug concrete, and it is backfilled by sand or excavated approved material. Sometimes water can be used instead of sand/excavated material.
Top plug:
It is a concrete layer of thickness around 500mm, as mentioned in design and drawing. Top plug provided over the filling and inside the well dredge hole.
Well cap:
A Well cap is a thick concrete mat that rests on the top of well stening. It is a part of the foundation and used to distribute loads of superstructure over the steining.

Field data required for Design of Wells:
- Design discharge from an authentic source
- Water surface slope on upstream and downstream
- Low water level and high flood level from an authentic source
- Silt factor from geotechnical investigation report
- Cross-section of the river
- Plain table survey of the river
- The deepest existing scour in the vicinity of the river.
- Strata chart i.e. bore log data.
- Availability of construction materials
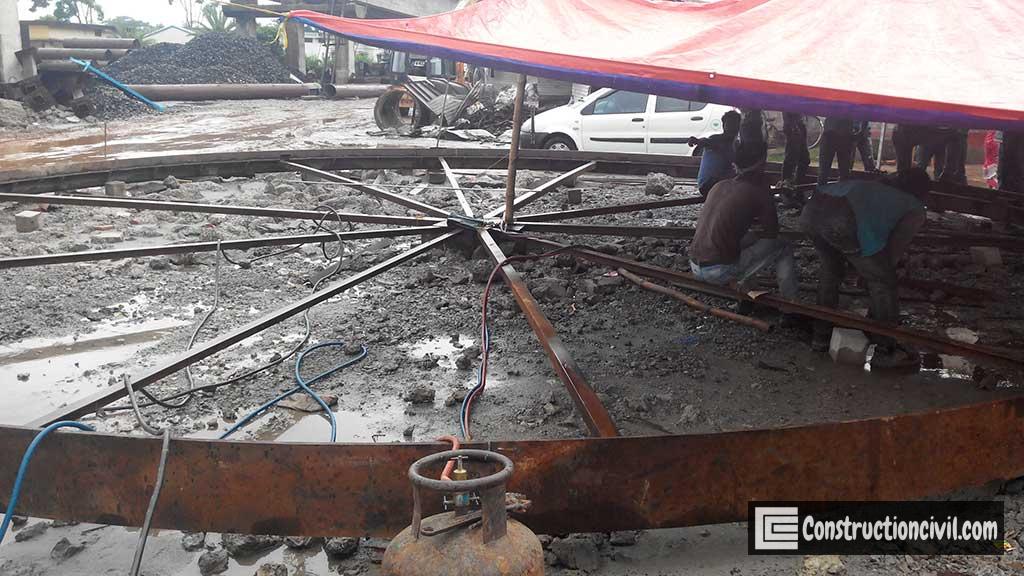
Construction Sequence of Well Foundation:
Following steps in the sequence are to be executed:
- Setting out
- Cutting edge – fabrication, transportation, assembly, placing in final position
- Well curb construction – inner shuttering, reinforcement work, outer shuttering, concreting, curing, de-shuttering and grounding.
- Construction of steining and sinking
- Checking and monitoring tilt and shift
- Bottom Plugging, sand filling, top/intermediate plugging, if any, water filling, if any, and casting of well cap





